Computer Functional Units & Memory
1. Computer Functional Units
Computer ek machine hai jo input leta hai, process karta hai, store karta hai aur output deta hai. Iska kaam smooth chalane ke liye computer ko kuch major parts me divide kiya gaya hai, jise Functional Units bolte hain.
Major Functional Units:
-
Input Unit
-
Output Unit
-
Memory Unit (Storage Unit)
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Input Unit
Input Unit wo part hai jisse computer user se data aur instructions receive karta hai. Matlab user jo type, click, scan, speak ya touch karta hai, vo sab Input Unit ke through computer tak pahunchta hai.

Simple Examples:
-
Keyboard se type karna → Input
-
Mouse click → Input
-
Scanner se photo scan → Input
-
Microphone me bolna → Input
Main Tasks of Input Unit:
-
User se data lena (text, click, audio, image)
-
Data ko binary (0 aur 1) me convert karna
-
Data ko Memory ya CPU tak bhejna
Popular Examples:
-
Keyboard
-
Mouse
-
Scanner
-
Microphone
-
Touch Screen
Real Life Example:
Jab Google me search karte ho:
-
Keyboard → Input deta hai
-
Computer → Process karta hai
-
Screen → Output dikhati hai
Output Unit
Output Unit wo part hai jo computer ke processed results user tak pahunchata hai. CPU data ko process karta hai aur Output Unit us result ko screen, paper ya speaker me show karta hai.

Simple Examples:
-
Monitor par YouTube video chal rahi hai → Output
-
Printer se document print ho raha hai → Output
-
Speaker se song baj raha hai → Output
Main Tasks of Output Unit:
-
CPU se processed data receive karna
-
Binary data ko human-readable form me convert karna
-
Result ko user tak pahunchana (text, image, sound, video)
Popular Examples:
-
Monitor
-
Printer
-
Speaker
-
Projector
Real Life Example:
-
CPU data process karta hai
-
Monitor output show karta hai
2. Storage Unit (Memory Unit)
Computer ka Storage Unit wo part hai jo data ko store, hold aur manage karta hai — chahe data temporary ho ya permanent. Ye computer ke performance ko directly affect karta hai.

Types of Storage Unit
-
Primary Memory (Fast but Temporary)
-
Secondary Memory (Slow but Permanent)
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary Memory ya Main Memory wo working area hai jaha data instant processing ke liye rakha jata hai.
Key Points:
-
CPU ke paas hoti hai → fast
-
Temporary storage
-
Computer off hote hi data delete ho jata hai
-
Program execution ke time use hoti hai
Types of Primary Memory:
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
-
CPU directly access karta hai
-
Fast memory
-
Temporary (PC off → data gone)
-
Multi-tasking depend karta hai RAM size par
-
Example: Chrome, VS Code, Games load hoti hai RAM me

2. Cache Memory
-
RAM se bhi fast
-
CPU ke andar (L1/L2) ya CPU ke bahar (L3)
-
Stores frequently used data for fast access
-
Example: Repeated calculations stored in Cache → CPU speed boost

Secondary Memory (Permanent Storage)
Secondary Memory me data permanently store hota hai. Chahe computer band ho jaye, data safe rehta hai.
Key Points:
-
Permanent storage
-
Slower than primary memory
-
High storage capacity
-
Example: Files, videos, apps, OS
Types of Secondary Memory:
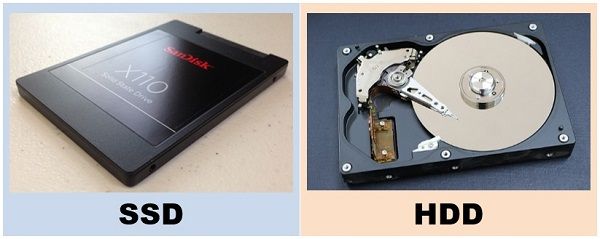
1. HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
-
Mechanical disks inside
-
Large capacity (500GB, 1TB)
-
Slower due to moving parts
-
Cheaper
-
Example: Movies, big files

2. SSD (Solid State Drive)
-
No moving parts → very fast
-
OS boot time 5–10 seconds
-
Durable & permanent
-
Expensive
-
Example: Fast boot, instant app opening

Primary vs Secondary Memory (Short Summary)
-
Primary: Temporary, Fast, Direct CPU access, Example: RAM, Cache
-
Secondary: Permanent, Slow, Indirect access, Example: HDD, SSD
Real-Life Example:
-
Movie file saved on HDD/SSD (Permanent)
-
Play karte waqt → RAM me load (Temporary)
-
Repeat scenes → Cache me stored (Super Fast)
Yehi hai Computer Functional Units aur Storage Unit ka complete concept Hinglish me, bilkul easy aur exam-ready explanation ke saath.
Comments
Post a Comment