Computer Functional Units & Memory
1. Computer Functional Units
A computer is a machine that takes input, processes it, stores it, and gives output. To make its work smooth, the computer is divided into major parts called Functional Units.
Major Functional Units:
Input Unit
Output Unit
Memory Unit (Storage Unit)
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Input Unit
The Input Unit is the part that receives data and instructions from the user. Whatever the user types, clicks, scans, speaks, or touches reaches the computer through the Input Unit.

Simple Examples:
- Typing on the keyboard → Input
- Mouse click → Input
- Scanning a photo using a scanner → Input
- Speaking into a microphone → Input
Main Tasks of Input Unit:
- Receive data from the user (text, click, audio, image)
- Convert data into binary (0s and 1s)
- Send data to Memory or CPU
Popular Examples:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Scanner
- Microphone
- Touch Screen
Real Life Example:
When you search on Google:
- Keyboard → provides Input
- Computer → Processes the data
- Screen → Shows Output
Output Unit
The Output Unit is the part that delivers the processed results from the computer to the user. The CPU processes the data and the Output Unit shows the result on a screen, paper, or speaker.

Simple Examples:
- YouTube video playing on a monitor → Output
- Document printing from a printer → Output
- Song playing through a speaker → Output
Main Tasks of Output Unit:
- Receive processed data from CPU
- Convert binary data into human-readable form
- Deliver the result to the user (text, image, sound, video)
Popular Examples:
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speaker
- Projector
Real Life Example:
- CPU processes data
- Monitor shows the output
2. Storage Unit (Memory Unit)
The Storage Unit of a computer is the part that stores, holds, and manages data — whether temporary or permanent. It directly affects the computer's performance.

Types of Storage Unit
- Primary Memory (Fast but Temporary)
- Secondary Memory (Slow but Permanent)
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary Memory or Main Memory is the working area where data is kept for instant processing.
Key Points:
- Located near the CPU → fast
- Temporary storage
- Data is lost when the computer is turned off
- Used during program execution
Types of Primary Memory:
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
- Directly accessed by CPU
- Fast memory
- Temporary (Data lost when PC is off)
- Multi-tasking depends on RAM size
- Example: Chrome, VS Code, games load into RAM

2. Cache Memory
- Faster than RAM
- Located inside CPU (L1/L2) or outside CPU (L3)
- Stores frequently used data for fast access
- Example: Repeated calculations stored in Cache → CPU speed boost

Secondary Memory (Permanent Storage)
Secondary Memory stores data permanently. Even if the computer is turned off, the data remains safe.
Key Points:
- Permanent storage
- Slower than primary memory
- High storage capacity
- Example: Files, videos, apps, OS
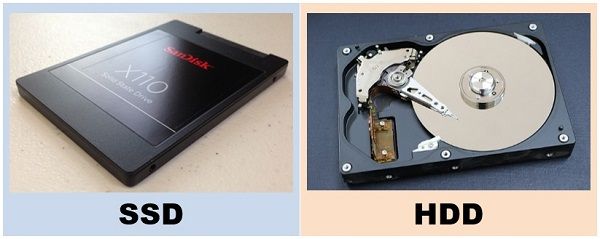
Types of Secondary Memory:
1. HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- Mechanical disks inside
- Large capacity (500GB, 1TB)
- Slower due to moving parts
- Cheaper
- Example: Movies, large files

2. SSD (Solid State Drive)
- No moving parts → very fast
- OS boot time 5–10 seconds
- Durable & permanent
- Expensive
- Example: Fast boot, instant app opening

Primary vs Secondary Memory (Short Summary)
- Primary: Temporary, Fast, Direct CPU access, Example: RAM, Cache
- Secondary: Permanent, Slow, Indirect access, Example: HDD, SSD
Real-Life Example:
- Movie file saved on HDD/SSD (Permanent)
- While playing → Loaded into RAM (Temporary)
- Repeated scenes → Stored in Cache (Super Fast)
This is the complete concept of Computer Functional Units and Storage Unit in English, with an easy and exam-ready explanation.
Comments
Post a Comment