Data Structure Ka Parichay Aur Prakar (Introduction and Types of Data Structure)
1. Data Structure Ki Definition
Data Structure ek logical aur systematic tareeka hai jisme data elements ko organize kiya jata hai taki essential operations jaise search, add aur delete efficiently kiye ja sake kam time aur memory mein.
Simple Example:
Ek library ko consider karo. Books (data) ko shelves (data structures) mein unke subjects ke hisaab se arrange kiya jata hai, taki jab aap koi book dhundho to turant mil jaye.
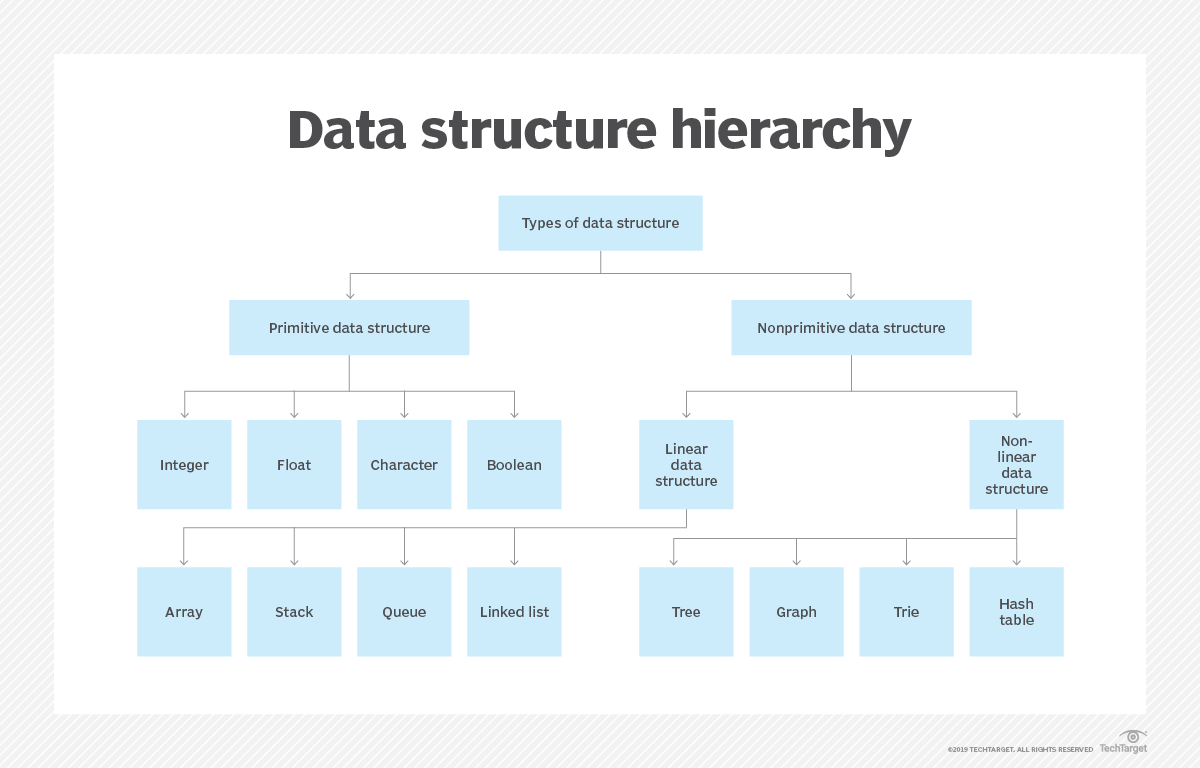
2. Data Structures Ke Prakar
Data Structures mainly do categories mein divide hote hain: Primitive aur Non-Primitive.
A. Primitive Data Structures
Ye basic data types hote hain jo directly machine level par kaam karte hain. Programming languages inhe pre-defined provide karti hain.
-
Integer (int): Poorn sankhyaon ko store karta hai. Example: 10, -5, 1000
-
Float/Double: Dashmlav sankhyaon ko store karta hai. Example: 3.14, 0.005
-
Character (char): Single akshar ya symbol store karta hai. Example: 'A', 'z', '9'
-
Boolean (bool): Do values store karta hai: True ya False. Example: True, False
B. Non-Primitive Data Structures
Ye complex structures hote hain jo primitive types ka use karke banaye jate hain. Inka main purpose data ke bade collections ko store karna aur unke relationships ko define karna hai.
i. Linear Data Structures
Data elements sequentially arranged hote hain, ek ke baad ek. Har element apne previous aur next element se connected hota hai.
-
Array: Fixed-size collection of elements of same type, contiguous memory locations mein store. Example: Class ke sabhi students ke marks store karna
-
Linked List: Elements (nodes) ka collection jisme har node data aur next node ka link rakhta hai. Example: Photo gallery mein photos ko next/previous buttons se connect karna
-
Stack: LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) principle pe kaam karta hai; add/remove ek end (top) se hota hai. Example: Undo/redo functionality software mein
-
Queue: FIFO (First-In, First-Out) principle pe kaam karta hai; data rear se add aur front se remove hota hai. Example: Printer job queue
ii. Non-Linear Data Structures
Data elements sequential order mein nahi hote. Ye hierarchical ya network form mein arranged hote hain aur complex relationships ko represent karte hain.
-
Tree: Hierarchical structure jisme root node hota hai aur child branches. Useful for representing hierarchies. Example: Computer ka file aur folder structure
-
Graph: Nodes (vertices) aur edges (connections) ka collection. Directed ya undirected, weighted ya unweighted ho sakta hai. Example: Cities aur routes Google Maps mein
-
Hash Table: Data ko key-value pairs mein store karta hai for fast access. Hash function keys ko positions pe map karta hai. Example: Dictionaries, caching, lookup tables
Details:
-
Tree: Root node top par, child nodes niche; har node multiple children hold kar sakta hai
-
Graph: Nodes edges se connected; networks, social connections, routes model kar sakta hai
-
Hash Table: Hash function use karke index compute karta hai; fast insertion, deletion, search operations possible. Fast lookup ke liye highly useful
3. Importance of Data Structures
-
Optimized Data Storage: Correct structure mein data store karne se memory save hoti hai
-
Fast Data Processing: Sahi structure choose karne se program ki speed aur efficiency improve hoti hai
-
Simplifies Problem Solving: Sorting, searching aur navigation jaise tasks efficiently solve karne mein help karta hai
-
Reusability & Maintainability: Ek baar implement karne ke baad multiple programs mein reuse karna easy hota hai, aur code maintain karna simple hota hai
Conclusion:
Data Structures programming ka foundation hain. Primitive aur non-primitive structures, including linear aur non-linear types jaise Trees, Graphs aur Hash Tables, samajhna essential hai for creating efficient, organized aur high-performance programs.
Comments
Post a Comment