Data Structures ke Main Operations
The main function of a Data Structure is to store and manage data. These are some basic operations that we perform on every data structure:
1. Traversal
What It Means: It means visiting each element of a data structure one by one.
Why We Do It: For example, printing all items of a list on the screen or checking each element.
Example: Visiting each number in an array from start to end.

2. Insertion
What It Means: Adding a new data element to a data structure.
Why We Do It: When you want to insert a new record (like a new student's name) into a list.
Example: Adding a new item (Push) on top of a Stack (like a pile of plates).
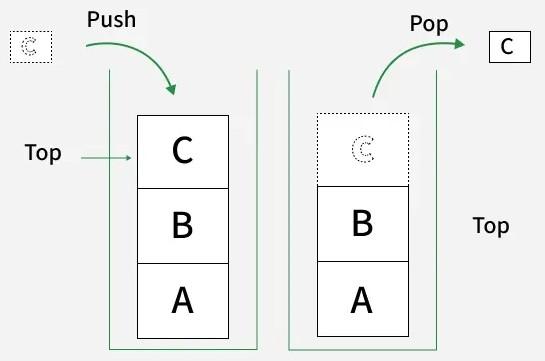
3. Deletion
What It Means: Removing an existing data element from a data structure.
Why We Do It: When a record is no longer needed or its validity has expired.
Example: Removing the first item (Dequeue) from a Queue (like a real-life line).

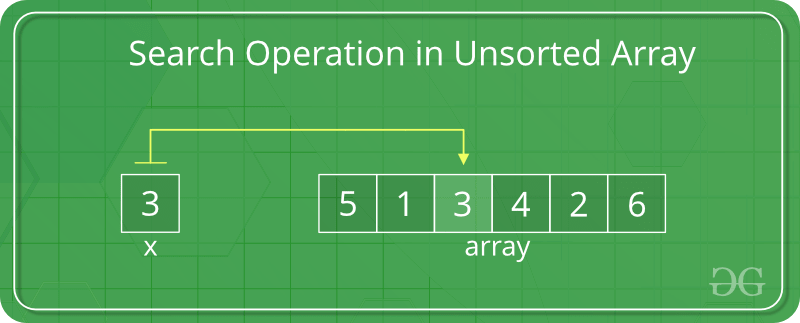
4. Searching
What It Means: Locating a specific element inside a data structure.
Why We Do It: Like searching for a particular contact number in a large phone book.
Example: Using Binary Search or Linear Search in an array.
5. Sorting
What It Means: Arranging data elements in a specific order (like Ascending or Descending).
Why We Do It: To search or display data more efficiently.
Example: Arranging students' marks from highest to lowest.

Applications of Data Structures (Real-life Usage)
Data Structures are used everywhere, wherever data needs to be managed inside a computer.
| Data Structure | Real-life Application (In Simple Words) |
| Array | Contact List: Storing all contacts in a sequence in a phone. |
| Linked List | Music Player Playlist: Songs are connected to each other so moving to next/previous is easy. |
| Stack | Undo/Redo Feature: Storing your last actions in a word processor. |
| Queue | Printer Task Line: The print command that comes first gets printed first. |
| Tree | File System: Hierarchical structure of files and folders in a computer. |
| Graph | Google Maps/GPS: Finding the shortest path between two locations. |
| Hash Table | Password Storage: Quickly verifying username-password pairs. |
Comments
Post a Comment