Data Structures: Linear vs. Non-linear
Data structures are the methods used to store and organize data in computer memory. They are divided into two main categories: Linear and Non-linear.
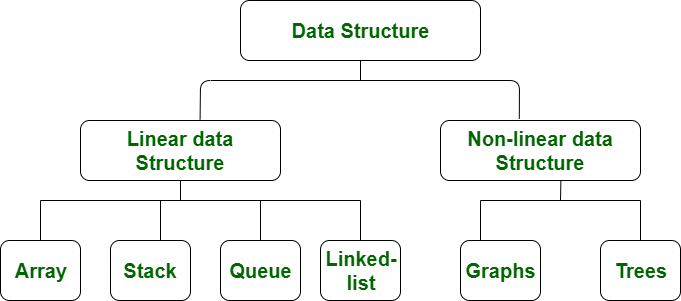
1. Linear Data Structures
When data elements are arranged in a sequence or one after another (in a sequential manner), it is called a Linear Data Structure. Each element has exactly one predecessor and one successor (except the first and last elements).
Arrangement: Elements are arranged in a straight line.
Traversal: Data elements can be traversed easily in a single run from start to end.
Implementation: Easy to implement and use.
-
Examples:
Array: A fixed-size sequential collection.
Linked List: Elements (nodes) are connected using pointers.
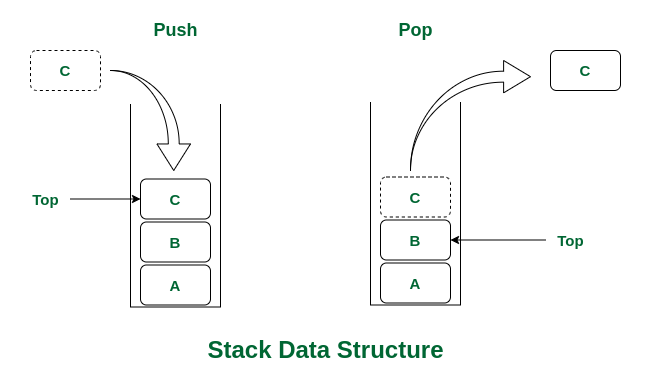
Stack: Works on the LIFO principle (Last In, First Out).
Queue: Works on the FIFO principle (First In, First Out).
2. Non-linear Data Structures

When data elements are not arranged sequentially, but instead follow a hierarchical or network structure, they are called Non-linear Data Structures. Elements may have multiple connections.
Arrangement: Elements are arranged in multi-level or random patterns.
Traversal: Traversal is more difficult because all branches and levels need to be considered. Algorithms like DFS/BFS are required.
Implementation: More complex than linear structures.
-
Examples:
Tree: Data is organized in a hierarchical (tree-like) form.
Graph: Represents complex relationships between data elements.
Main Differences
| Basis | Linear Data Structures | Non-linear Data Structures |
| Arrangement | Sequential (one after another) | Non-sequential (Hierarchical/Network) |
| Relationship | Each element has one predecessor and one successor (simple) | Elements can have multiple connections (complex) |
| Memory | Memory is continuous (as in arrays) | Memory can be used at random or distributed locations |
| Complexity | Generally less complex | Generally more complex |
| Examples | Array, Linked List, Stack, Queue | Tree, Graph |
Comments
Post a Comment