Microprocessor

What is a Microprocessor? (Definition)
A microprocessor is a small electronic chip that works like the brain of a computer. It is the main part of the CPU that handles all calculations, decision-making, and tasks.
In simple words: Microprocessor = A chip made up of millions of transistors that processes data.

History of Microprocessor (Short Introduction)
The first microprocessor was the Intel 4004 (1971). It had only 2300 transistors and was mainly used for calculators. Today’s processors use millions to billions of transistors and are super-fast.
How Does a Microprocessor Work?
A microprocessor follows three basic steps:
- Fetch: It brings the instruction from memory.
- Decode: It understands what task the instruction wants to perform.
- Execute: It performs calculations or executes the task.
All this happens billions of times per second — which is why we measure processor speed in GHz.
Main Components of a Microprocessor

- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit): Performs mathematical and logical operations.
- CU (Control Unit): Controls all other parts of the processor.
- Registers: High-speed temporary memory.
- Bus System: Transfers data, address, and control signals.
Types of Microprocessors
- 8-bit Microprocessor (Example: Intel 8085)
- 16-bit Microprocessor (Example: Intel 8086)
- 32-bit Microprocessor (Example: Intel Pentium)
- 64-bit Microprocessor (Example: AMD Ryzen, Intel i7/i9)
Applications of Microprocessor (Where It Is Used?)
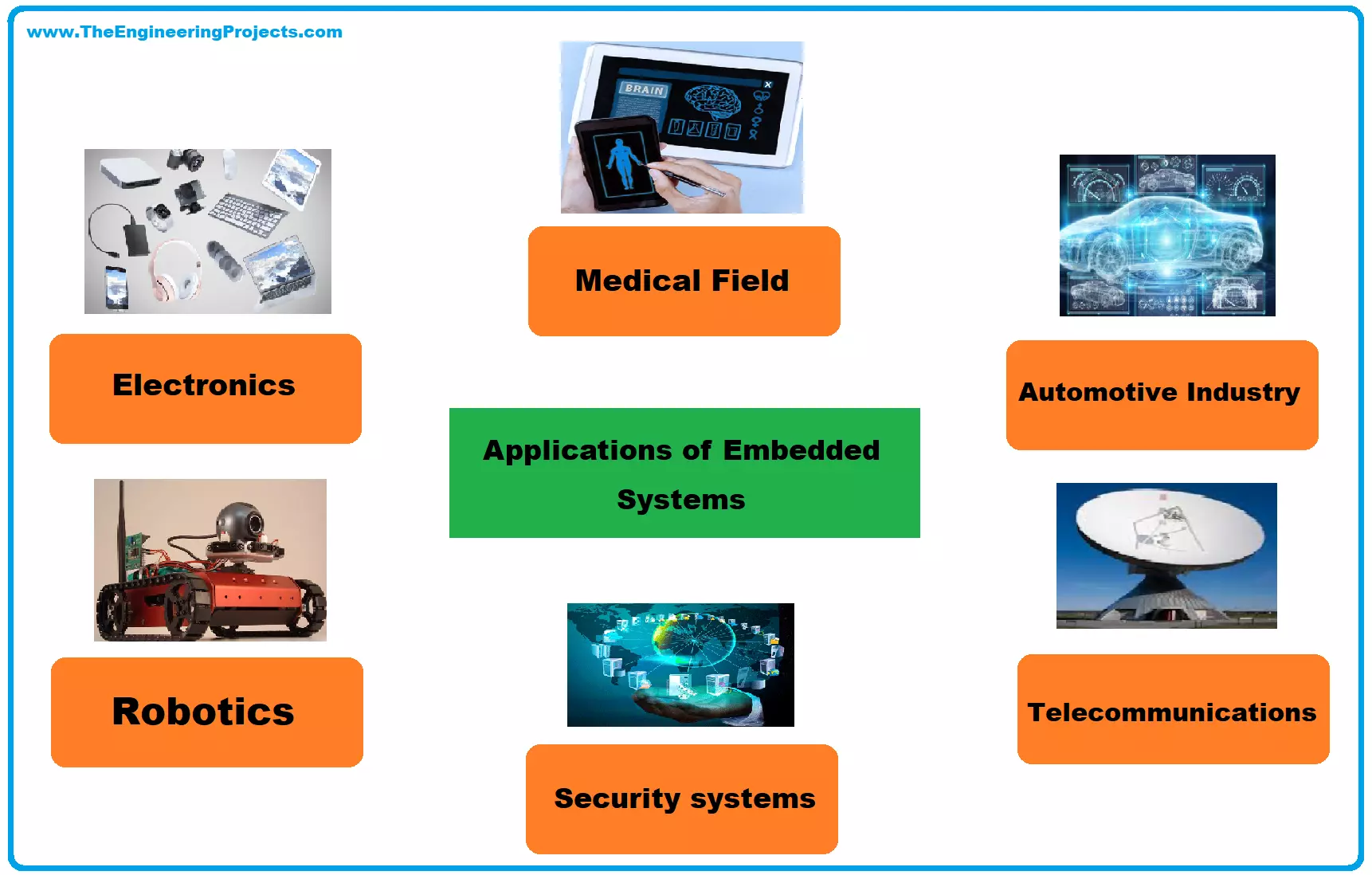
Microprocessors are used almost everywhere:
- Computers and Laptops
- Smartphones
- Smart TVs
- Cars (Engine control unit, sensors)
- Washing Machines
- ATM Machines
- Medical Devices
- Gaming Consoles
Advantages of Microprocessor
- Fast processing (billions of operations per second)
- Small size & low power consumption
- Easy to upgrade
- Reliable and efficient
- Ability to perform multiple tasks at the same time (multitasking)
Disadvantages of Microprocessor
- Overheating problem (requires fans or cooling system)
- Does not have human-like intelligence
- If corrupted or damaged, the entire system can fail
- Can be affected by viruses
Real-Life Examples Where Microprocessors Are Used
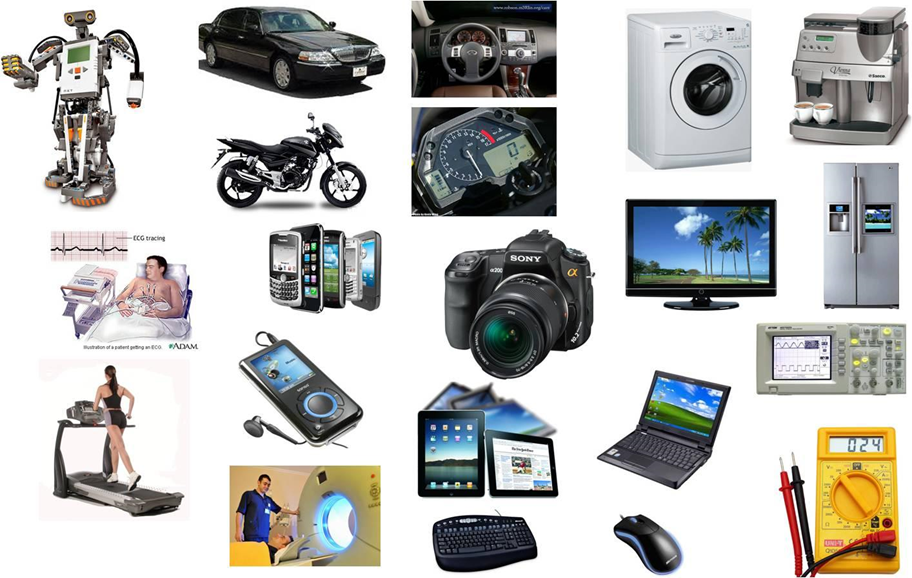

- Smartphone: Snapdragon / MediaTek processors.
- Car Engine: Microprocessors control fuel and ignition.
- Smart Watch: Sensors + microcontroller + processor.
- Home Appliances: AC, Fridge, Microwave, Washing Machine.
- Military Drones: Navigation + sensor processing.
Conclusion
A microprocessor is a small chip that makes the entire system smart. Every modern device cannot work without a microprocessor. It is the key component that makes devices fast, smart, and automated.
Comments
Post a Comment