Queue – FIFO, types: Simple, Circular, Priority, Deque
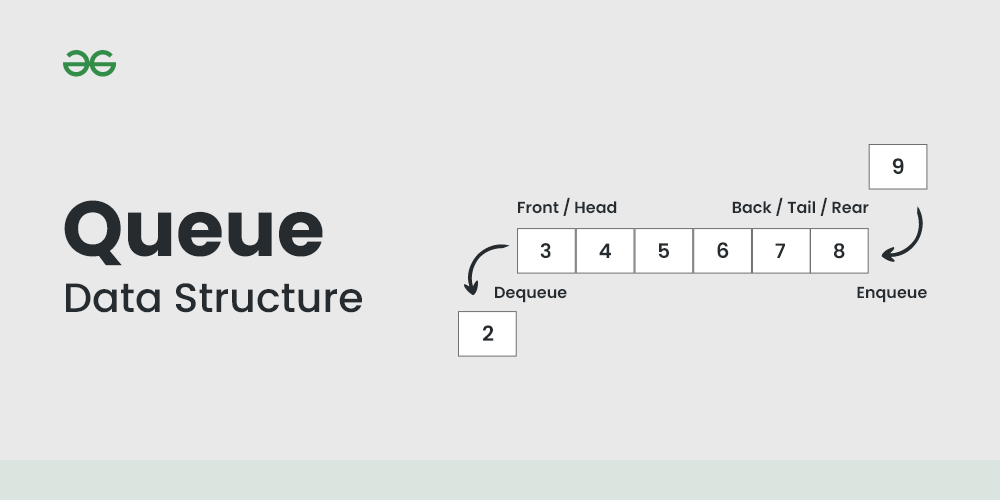
What is Queue (Queue)?
Queue (Queue) is also a Linear Data Structure like Stack, but it works in a different way from Stack.
You can imagine Queue as a line or queue (queue), like you see at a ticket counter or bus stop.
In Queue, data elements are managed from two different ends:
Front (Front): From where elements are removed.
Rear (Rear): Where new elements are inserted.
FIFO Principle (FIFO Principle)
Queue's basic working method (working principle) is based on FIFO.
FIFO's full form is: First In, First Out
What does it mean?: It means that the element which entered first (first) in the queue will be the one that comes out first from the queue.
Example: When you give several print commands to a printer, the printer processes those commands in the same order in which they came (FIFO).

Queue Operations (Queue Operations)
In Queue, mainly these two basic operations are there, which maintain its FIFO property:
1. Enqueue (Insert)
Work: Inserting (inserting) a new element at the Rear end of the queue.
Process: The Rear pointer moves one position forward, and the new element is stored there.
Condition: If the queue is completely full, it is called Queue Overflow, and no new element can be inserted.

2. Dequeue (Remove)
Work: Removing (removing) the element from the Front end of the queue.
Process: The Front pointer moves one position forward, and the element that was previously at Front is returned (returned).
Condition: If the queue is empty, it is called Queue Underflow, and no element can be removed.

Auxiliary Operations:
Front(): Viewing (accessing) the Front element only, without removing it.Rear(): Viewing the Rear element only, without removing it.isEmpty(): Check if the queue is empty.isFull(): Check if the queue is completely full.

Types of Queue (Types of Queue)
Queue is divided into several types based on its structure and working style:
1. Simple Queue (Simple Queue)
Identification: This is the standard FIFO queue implemented using a linear array.
Limitation (Problem): When Dequeue operations happen, empty space is created at the beginning (beginning) of the queue. But if the Rear pointer reaches the end of the array, we still cannot insert new elements, even if there is a lot of empty space at the beginning. This is called Memory Wastage or the problem of Linear Queue.
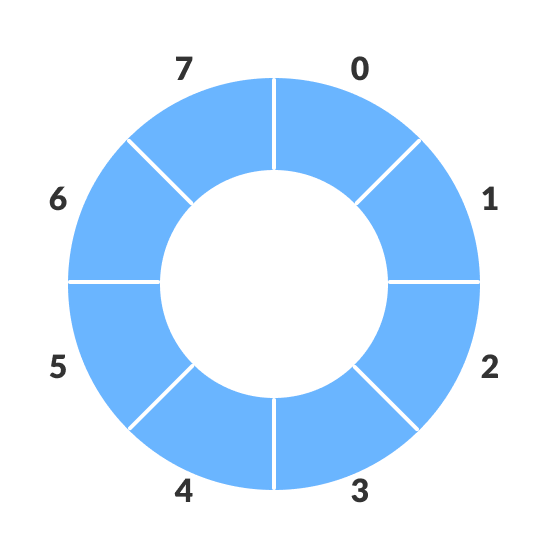
2. Circular Queue (Circular Queue)
Identification: This solves the Memory Wastage problem of Simple Queue.
Structure: In this, the last element of the array is conceptually connected to the first element, so it works in a circular manner.
Working: If the Rear pointer reaches the end of the array, it can wrap around (wrap around) to insert new elements from the empty space at the beginning (index 0), if there is space at Front.
Benefit: This allows better utilization of memory resources.
3. Priority Queue (Priority Queue)
Identification: This does not follow the FIFO principle. In this, each element has a Priority Value associated with it.
Working: Elements are removed not based on their arrival order, but according to their priority. The element with the Highest priority will come out first, no matter when it was inserted into the queue. If two elements have the same priority, they are removed in FIFO order.
Application: Scheduling tasks in Operating Systems (where high priority tasks get CPU time first).

4. Deque (Double Ended Queue)
Full Form: Double Ended Queue (Queue with two ends).
Identification: This is a queue in which elements can be inserted (Insert) and removed (Delete) from both ends (Front and Rear).
Types: Based on its flexibility, it can be used in two ways:
Input Restricted Deque: Elements are inserted from only one end, but can be removed from both ends (can be used like a Stack).
Output Restricted Deque: Elements are inserted from both ends, but removed from only one end.
Benefit: It provides the flexibility to be used like both Stack and Simple Queue.

Note: This blog post is made to explain the Queue Data Structure easily. If you want to know more, comment!
Comments
Post a Comment