What is an Array?
Array is another linear data structure, but it works quite differently from Linked List.
- Think of an Array as a shelf or continuous line of boxes.
- It stores data items of the same type (like only numbers, or only names) together, one after another (contiguously), in memory.
Memory Allocation (Memory Allocation)
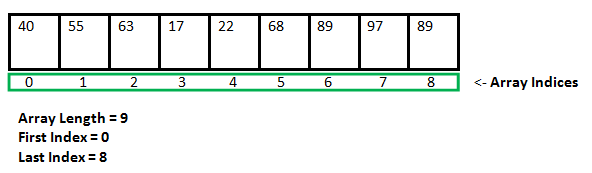
The most special thing about Array is that all its elements get adjacent (attached to each other) space in memory.
- If you have an Array with 5 elements, then these 5 elements will be placed together in a line in memory.
- This makes data access very fast.
Indexing (Indexing)
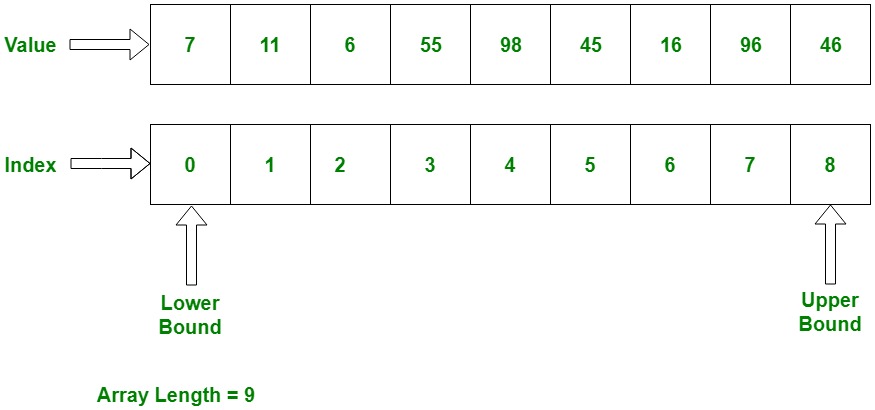
Each element of the Array is identified by its position, which is called Index (Index).
- Indexing always starts from 0 (zero).
- If the Array's size is 'N', then indices will be from `0, 1, 2, ..., N-1`.
Example: If your Array's name is `Marks` and it has 5 elements: `[85, 92, 78, 65, 99]`
| Value (Value) | 85 | 92 | 78 | 65 | 99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index (Index) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
You can access the value `78` directly by saying `Marks[2]`.
Types of Array (Types of Array)

Array is classified based on its dimensions:
1. One-Dimensional Array (1D Array)
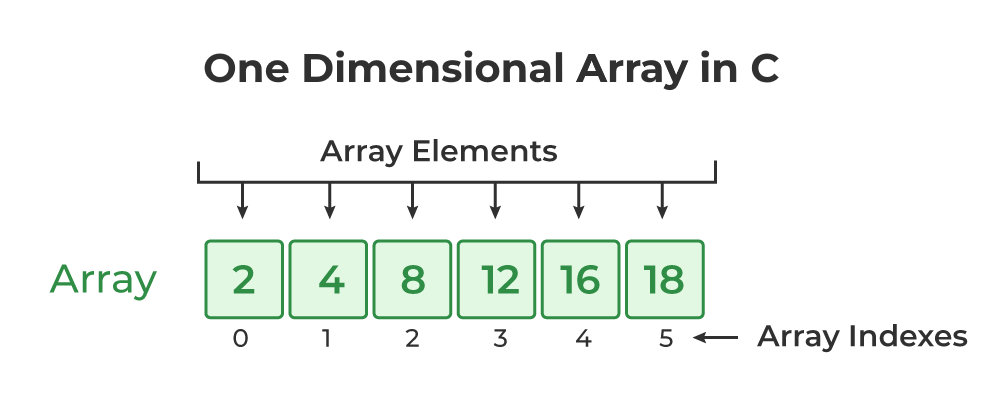
- This is the simplest array, which is like a single row or column.
- To access it, only one index is needed (like: `Marks[i]`).
2. Multi-Dimensional Array (2D/3D Array)
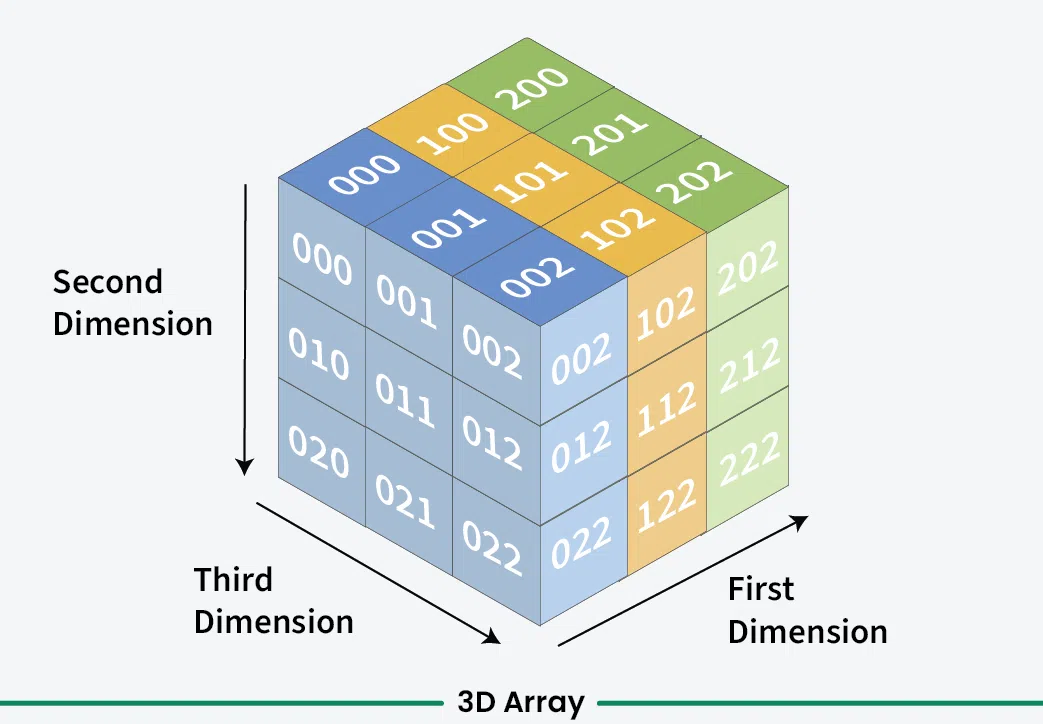
- Two-Dimensional Array (2D Array): Think of it as a Matrix (Matrix) or Table (Table), which has Rows and Columns.
- To access it, two indices are needed (like: `Matrix[row][column]`).
- Three-Dimensional Array (3D Array): This is like a collection of 2D Arrays, like stacked plates.
Array Operations (Array Operations)
The common operations on Array are:
1. Traversal (Traversal)
- Starting from Index 0, visiting each element of the array one by one up to the last index.
2. Insertion (Insertion)
- Adding a new element to the Array.
- Challenging Part: Since the Array's size is fixed, if the array is full, then before insertion, the old elements have to be shifted, or a new, larger array has to be created.
3. Deletion (Deletion)
- Removing an element from the Array.
- Challenging Part: After the element is deleted, the elements after it have to be shifted one position back so that the memory remains continuous.
4. Search (Search)
- Finding a specific value in the Array. This can be Linear Search (checking one by one) or Binary Search (if the array is sorted, then very fast).
5. Update (Update)
- Changing the value of the element present at some index. (Like: `Marks[3] = 70`)
Difference between Array and Linked List (Summary)
| Feature | Array | Linked List |
|---|---|---|
| Size (Size) | Static (usually fixed), or dynamic Array (but slow). | Dynamic (easily grows/shrinks). |
| Memory Allocation | Contiguous (one after another, continuous space). | Non-Contiguous (anywhere, linked by pointers). |
| Accessing (Accessing) | Random Access (Very Fast, O(1)). Can access directly via index. | Sequential Access (Slow, O(n)). Have to start from Head. |
| Insertion/Deletion | Slow (O(n)) because shifting has to be done. | Fast (O(1)) if the node's address is known. |
| Memory Usage | Efficient (no pointer overhead). | Overhead (extra memory for pointers). |
Advantages of Array (Advantages)
- Fast Access (Fast Access): Due to Random Access, you can access any element instantly (O(1) time).
- Memory Locality: All elements are together, so CPU Cache works well and performance increases.
Disadvantages of Array (Disadvantages)
- Fixed Size (Fixed Size): The size of most Arrays has to be defined beforehand. If more data comes, space may fall short.
- Slow Insertion/Deletion (Slow Insertion/Deletion): When inserting or deleting something in the middle, many elements have to be shifted, which is time-consuming.
- Memory Waste: If you have created a large array, but stored less data in it, then the remaining memory wastes.
Comments
Post a Comment