What is Stack (LIFO, Operations, Applications)
Stack is a very fundamental (basic) and linear (linear) Data Structure, which means that data elements are stored in a sequence (sequence).
The biggest identity of Stack is that in it, the work of inserting data (insertion) and removing data (deletion) happens only from one end, which we call Top (top).
LIFO Principle (LIFO Principle)
Stack's execution, meaning its working method, is based on the LIFO principle.
- LIFO's full form is: Last In, First Out
- What does it mean?: Its direct meaning is that the element (element) which was inserted last (last) in the stack will be the one removed first (first) from the stack.
Simple Analogy (Example):
Imagine a pile of coins (pile of coins). When you insert a new coin, it always goes to the top (Last In). When you remove a coin, you always remove the topmost coin (First Out).

Stack Operations (Stack Operations)
In Stack, primarily (primarily) there are three operations, which are always performed at the Top of the stack:
A. Basic Operations
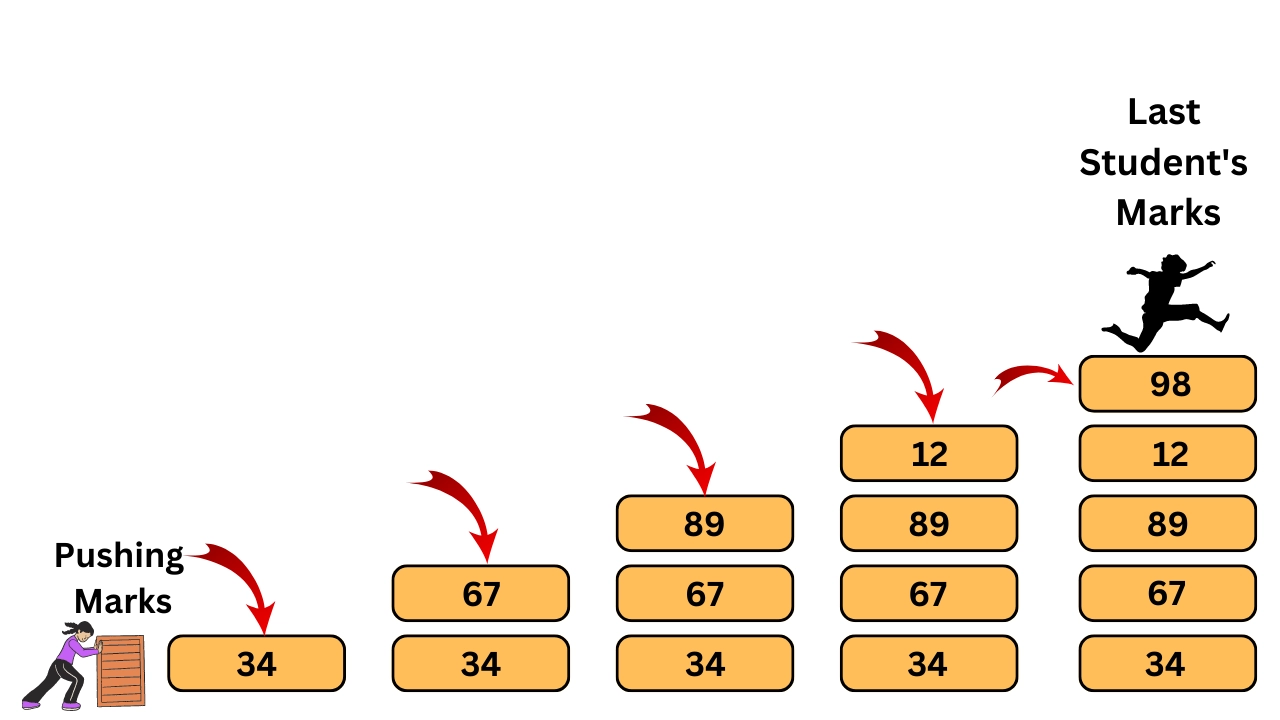
1. Push (Insert)
- Work: The operation of inserting (inserting) a new item at the top of the stack.
- Mechanism: When
Pushhappens, the Top pointer moves one position up and the new item is placed at that position. - Condition: If the stack is completely full (meaning there is no more space in it), this situation is called Stack Overflow, and the
Pushoperation cannot be performed.
.webp)
2. Pop (Remove)
- Work: The operation of removing (removing) the item from the top of the stack.
- Mechanism: When
Pophappens, the top item is returned (returned), and the Top pointer moves one position down. - Condition: If the stack is empty (meaning there is no item in it), this situation is called Stack Underflow, and the
Popoperation cannot be performed.
.webp)
B. Auxiliary Operations
3. Peek / Top (View)
- Work: The operation of viewing (accessing) which item is at the Top of the stack, without removing (removing) it.
- Benefit: With this, we can check the Top item without changing the Stack's structure.
4. IsEmpty (Is Empty?)
- Work: Check whether there is no item in the stack.
- Benefit: This is necessary for checking before Underflow occurs.

5. IsFull (Is Full?)
- Work: Check whether there is no more space in the stack (if the stack is of fixed size).
- Benefit: This is necessary for checking before Overflow occurs.

Stack Applications (Stack Applications)
The use of Stack is to manage many important things in Computer Science and Programming:
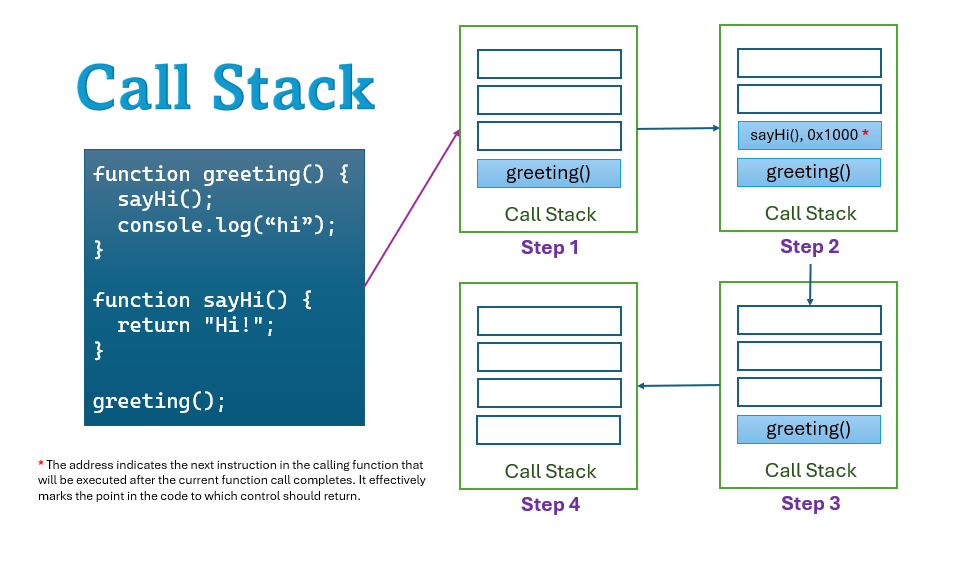
1. Function Call Management (Call Stack)
- Whenever a program runs and one function calls another function, that execution order is managed in a special stack called the Call Stack.
- The information of each function call (return address, local variables, etc.) is pushed. When the function ends, its information is popped. LIFO ensures that control goes back to the right place.
2. Expression Conversion and Evaluation (Expression Evaluation)
- Use: To convert Infix expressions (like A + B * C) to Postfix (Reverse Polish Notation) or Prefix (Polish Notation).
- Why Stack? Stack tracks operator precedence (priority of operators) and manages brackets, so that the evaluation (evaluation) of expressions happens in the correct order.
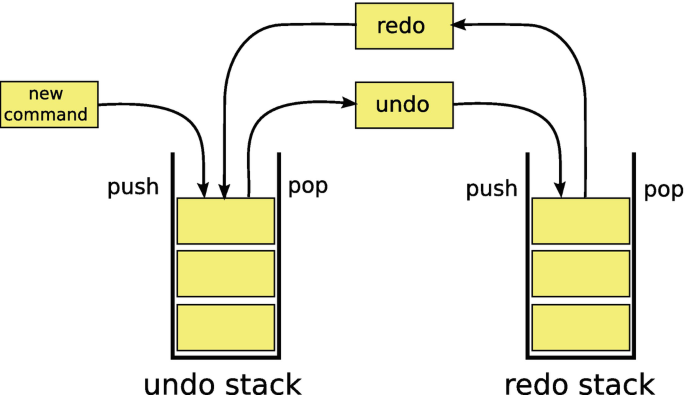
3. Undo / Redo Mechanism (Undo / Redo Mechanism)
- In text editors (like MS Word) and graphic software, undo and redo options work with the help of Stack.
- Each action (like typing, deleting) is pushed into the Undo Stack. When you Undo, the action is popped. A separate stack is used for Redo.
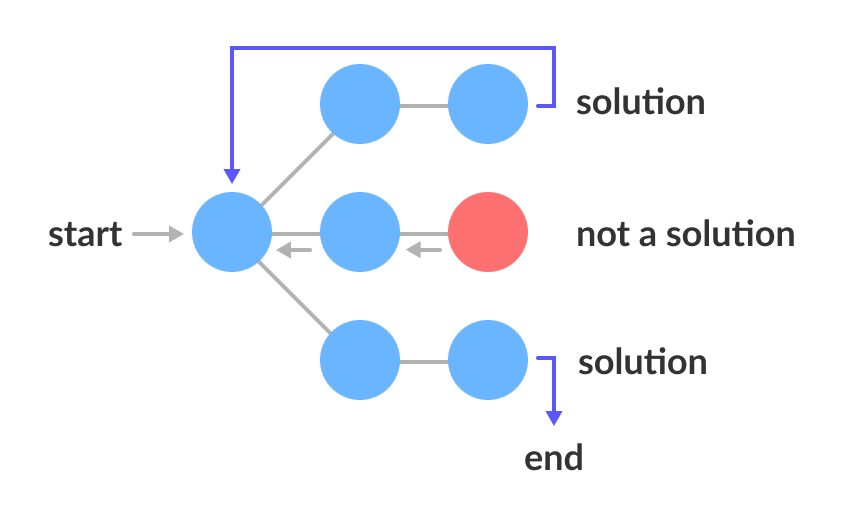
4. Backtracking Algorithms (Backtracking Algorithms)
- Use: When we need to explore all possible paths (all possible routes) (like solving Sudoku or Maze-solving).
- When we move forward on a path, we push the state. If that path turns out to be wrong (dead end), we pop and go back (backtrack) to the previous correct path.
5. Recursion (Recursion)
- When a function calls itself repeatedly (Recursion), internally this process uses the Call Stack.
Note: This blog post is made to explain the Stack Data Structure easily. If you want to know more, comment!
Comments
Post a Comment