What is a Linked List?
Linked List is a linear data structure, which is slightly different from an Array.
- In an Array, data items are stored continuously one after another in memory locations.
- However, in a Linked List, data items (called Nodes) can be scattered (anywhere) in memory.
The main idea of a Linked List is that every data item (i.e., Node) also holds the address (location) of the next data item.
What is a Node? (What is a Node?)
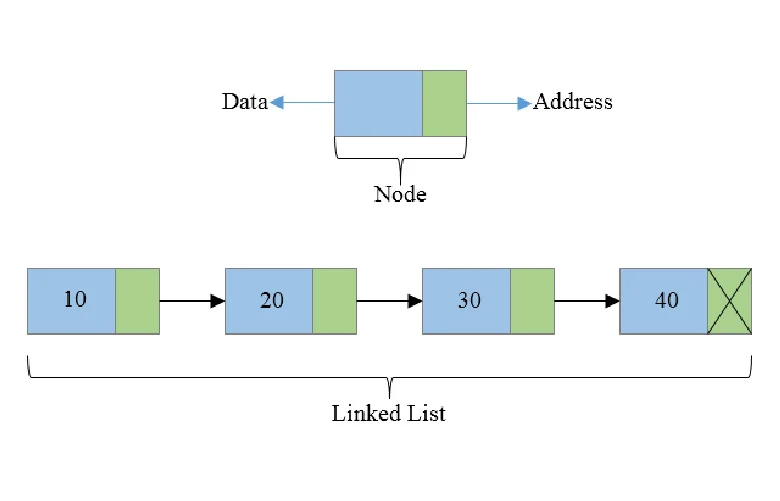
Every element of a Linked List is called a Node. Each Node has two main parts:
- Data Field (Data Field):
- The actual data is stored here (like any number, name, etc.).
- Next Field (Next Field) / Pointer:
- The address of the next Node is stored here.
- If this is the last Node, its Next Field is always NULL (or None), meaning there is no element after it.
Concept of Linked List

- Start/Head (Start/Head): The first Node of the list is called the Head. We must always know the address of the Head, as this is where the list begins.
- End/Tail (End/Tail): The Next Field of the last Node of the list is always NULL.
Remember: Nodes are linked to each other through pointers.
Types of Linked List (Types of Linked List)

Linked Lists are primarily of three types:
1. Singly Linked List (Singly Linked List)
.webp)
- This is the most simple type.
- Each Node has one Data field and one Next pointer, which points to the next node.
- We can only travel (traverse) in the forward direction.
2. Doubly Linked List (Doubly Linked List)

- Each Node here has three parts: Data, Next pointer, and Previous (Prev) pointer.
- The Next pointer points to the next node.
- The Prev pointer points to the previous node.
- This allows us to travel in both forward and backward directions in the list.
3. Circular Linked List (Circular Linked List)
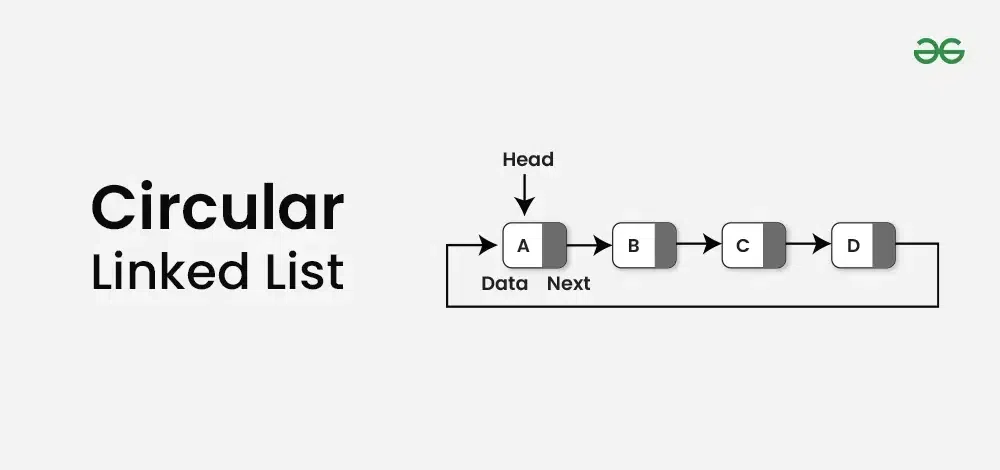
- It can be Singly or Doubly.
- Its special feature is that the Next pointer of the Last Node is not NULL, but it points to the First Node (Head).
- This makes the list a circle or loop.
Operations on Linked List (Linked List Operations)
The common operations (actions) on a Linked List are:
1. Insertion (Insertion)
- Adding a new Node to the list. This can be at the beginning, end, or in the middle (at a specific position).
2. Deletion (Deletion)
- Removing an existing Node from the list. This can also be at the beginning, end, or in the middle.
3. Traversal (Traversal)
- Starting from the Head, visiting each Node in the list once. This is to know what data is in the list.
4. Search (Search)
- Finding a Node with a specific data value in the list.
Difference between Array and Linked List (Array vs. Linked List)
| Feature | Linked List | Array |
|---|---|---|
| Size (Size) | Dynamic (can grow or shrink as needed). | Static (fixed size), or dynamic in some languages (but implementation differs). |
| Memory Allocation | Allocated at run-time (Dynamic Allocation). | Allocated at compile-time or run-time. |
| Accessing (Accessing) | Sequential Access (have to move forward one by one from the start). | Random Access (can access any index directly). |
| Insertion/Deletion | Fast (O(1)) if the Node's address is known. | Slow (O(n)) because elements need to be shifted. |
| Memory Usage | Extra memory is used for pointers besides data. | No extra memory is used for pointers. |
Advantages of Linked List (Advantages)
- Dynamic Size (Dynamic Size): Can easily grow or shrink as needed, no memory waste.
- Easy Insertion/Deletion (Easy Insertion/Deletion): No need to shift nodes, just change the pointers, which is faster.
Disadvantages of Linked List (Disadvantages)
- Memory Overhead: Extra memory is required to store pointers.
- No Random Access: You do not have permission to access any element directly based on index; you always have to start from the Head and move in sequence.
Comments
Post a Comment