What is a Tree
A tree is a non-linear data structure where data is stored in a hierarchical manner.
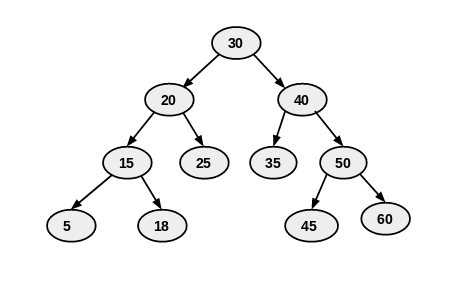
- The topmost node in a tree is called the Root (like 30 in your image).
- Each node can have zero or more child nodes.
- Nodes that connect to other nodes are called parent nodes.
- Nodes with no children are called leaf nodes (like: 5, 18, 25, 35, 45, 60).
The image you provided is a Binary Search Tree (BST), in which:
- Each node can have a maximum of two children.
- The value of the left child is less than the parent.
- The value of the right child is greater than the parent.
What is Tree Traversal?
Tree traversal means visiting each node in the tree once. There are different ways to traverse, allowing us to process nodes in a specific order.
The three main ways to traverse a binary tree are: In-order, Pre-order, and Post-order. All three are types of Depth First Search (DFS).
1️⃣ Pre-order Traversal
Definition:
In pre-order traversal, we first visit the root node, then traverse the left subtree, and finally the right subtree.
In pre-order traversal, we first visit the root node, then traverse the left subtree, and finally the right subtree.
- Order: Root → Left → Right
- Visit the Root node. (Print the data)
- Recursively call Pre-order on the Left subtree.
- Recursively call Pre-order on the Right subtree.
On Your Example Tree:

- Root: 30
- Left Subtree (Root 20): 20 → 15 → 5 → 18 → 25
- Right Subtree (Root 40): 40 → 35 → 50 → 45 → 60
Result:
30, 20, 15, 5, 18, 25, 40, 35, 50, 45, 60
2️⃣ In-order Traversal
Definition:
In in-order traversal, we first traverse the left subtree, then visit the root node, and finally the right subtree.
In in-order traversal, we first traverse the left subtree, then visit the root node, and finally the right subtree.
- Order: Left → Root → Right
- Recursively call In-order on the Left subtree.
- Visit the Root node. (Print the data)
- Recursively call In-order on the Right subtree.
Important Note: In a BST, in-order traversal always gives values in sorted order.
On Your Example Tree:

- Left Subtree (Root 20): 5 → 15 → 18 → 20 → 25
- Root: 30
- Right Subtree (Root 40): 35 → 40 → 45 → 50 → 60
Result:
5, 15, 18, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 60
3️⃣ Post-order Traversal
Definition:
In post-order traversal, we first traverse the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally visit the root node.
In post-order traversal, we first traverse the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally visit the root node.
- Order: Left → Right → Root
- Recursively call Post-order on the Left subtree.
- Recursively call Post-order on the Right subtree.
- Visit the Root node. (Print the data)
On Your Example Tree:

- Left Subtree (Root 20): 5 → 18 → 15 → 25 → 20
- Right Subtree (Root 40): 35 → 45 → 60 → 50 → 40
- Root: 30
Result:
5, 18, 15, 25, 20, 35, 45, 60, 50, 40, 30
Comments
Post a Comment