Why C is called a middle-level language?
Why is C Called a Middle-Level Language?
C language is called a middle-level language because it contains features of both high-level languages (such as Python, Java) and low-level languages (such as Assembly).
It gives the programmer the ability to perform both types of tasks:
- High-Level Abstraction: C provides structures like functions, loops, and variables that make the code readable and understandable.
- Low-Level Access: C allows direct memory manipulation (meaning accessing memory directly) and hardware-level management — which is generally done by low-level languages.
High-Level Language Features
C contains features that make programming efficient and keep the developer away from hardware-level details:
- Portability: Code written in C can run on different machines with minor changes.
- Structured Programming: C uses control structures such as if-else, for, and while, which make the code well-organized and easier to maintain.

Low-Level Language Features
C has powerful low-level tools that make it perfect for system programming (operating systems, device drivers, embedded systems):
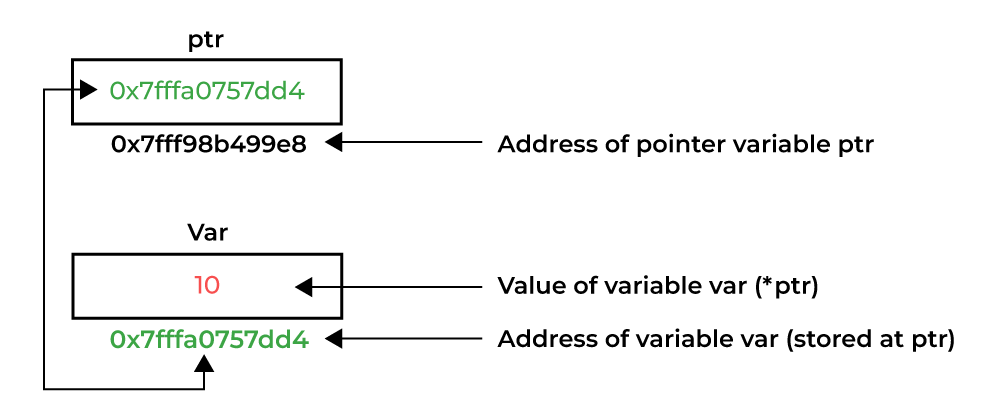
- Pointers: The most important feature of C is pointers. With the help of pointers, the programmer can directly work with memory addresses. This is extremely important for efficient memory management.
- Bit-Level Manipulation: C provides the ability to manipulate data at the bit and byte level. This is essential for device drivers, embedded systems, and operating system development.
Conclusion
C language provides a perfect balance between high-level abstraction (where writing code is simple) and low-level functionality (where the programmer has full control over hardware and memory).
This is why C is widely used in building Operating Systems (such as UNIX), Compilers, and Device Drivers, and therefore it is known as a middle-level language.
Comments
Post a Comment